Phishing scammers took over the X account of L1 community VeChain following assaults on Rocket Pool, Coingecko, and Polychain Capital’s CEO inside a number of days.
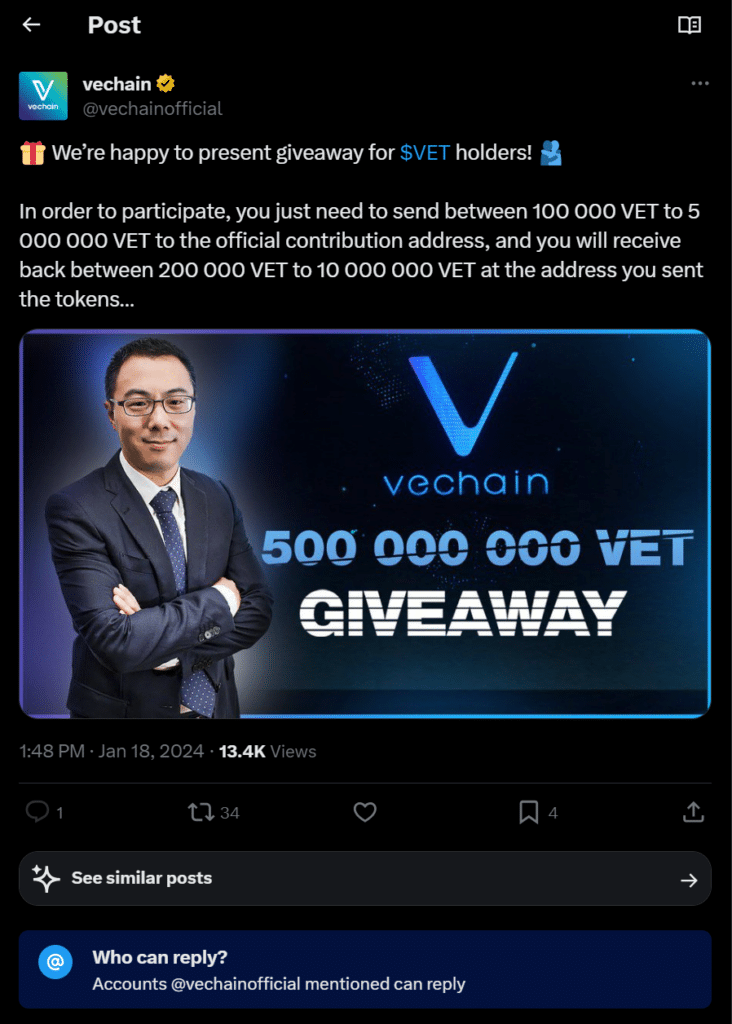
VeChain’s X web page offered a supposed giveaway for VET holders with a phony contribution handle connected. Customers had been directed to ship as a lot as $15,000 in VET cash to take part within the promo. In trade, they’d obtain a most of $300,000 in VeChain’s native blockchain token.
The scammer leveraged the picture of VeChain CEO Sunny Lu in a bid so as to add a layer of authenticity to the marketing campaign.
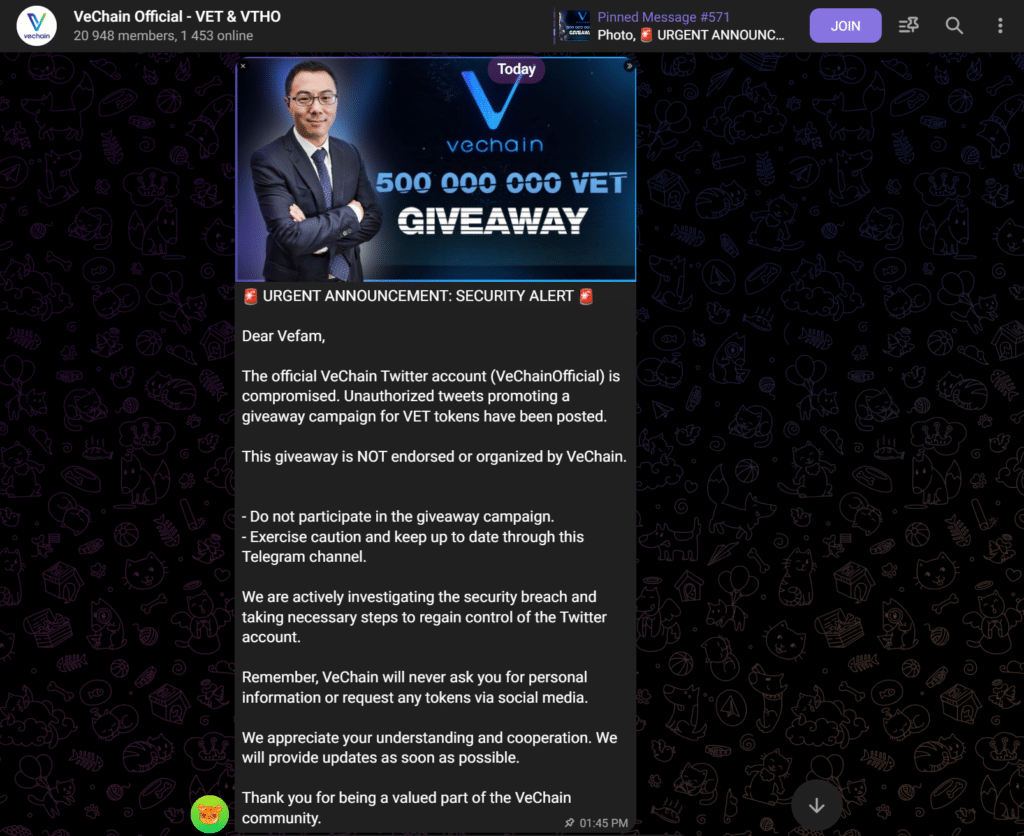
VeChain representatives on an official Telegram channel flagged the suspicious actions and alerted customers to the pitfall shortly after the web page was hacked. The malicious posts had spent a minimum of two hours on the challenge’s timeline.
crypto.information reached out to VeChain in regards to the compromise and was but to listen to again at press time. Nevertheless, the X web page appeared safe, and the pretend airdrops beforehand pinned and tweeted had been deleted. The value on VET traded lower than 1% down amid the incident per CoinMarketCap.
The Layer-1 blockchain is the most recent protocol to undergo a hack on its social media accounts throughout January. Yesterday, Rocket Pool’s X account was exploited by unknown scammers selling a pretend good contract flaw. Hackers instructed customers emigrate their property, however Rocket Pool admins on Discord cautioned towards clicking hyperlinks.
The X accounts of Coingecko and Polychain Capital CEO Olaf Carlson-Wee suffered comparable breaches, with hackers publishing dangerous hyperlinks meant to empty customers’ wallets. It’s attainable that these accounts had been breached attributable to an assault vector linked to 2FA with cell phone numbers.
Crypto hackers and phishing scammers have been tapping new methods to trick digital asset holders out of their digital currencies. Apart from straight hijacking high-profile accounts like Coingecko, hackers additionally mimic X pages by means of a consumer interface vulnerability.
The flaw reportedly permits unhealthy actors to generate illegitimate URLs containing malicious content material.

