Web3 safety consultants think about North Korea’s Lazarus Group essentially the most outstanding and complicated menace to the crypto trade in 2024.
Earlier this week, the notorious Lazarus Group reportedly funneled $12 million by crypto tumbler Twister Money. The funds have been allegedly linked to final November’s HTX and Heco Bridge hack, which noticed the platforms lose over $90 million.
Nonetheless, this wasn’t the group’s solely heist in 2023. All year long, the North Korea-backed hackers compromised over $400 million price of property throughout numerous crypto platforms, together with CoinEX, Poloniex, Stake.com, and Atomic Pockets. In 2022, the group was accountable for the largest defi hack in historical past, because it compromised the Ronin Community to steal roughly $620 million.
Lazarus’s hacks occurred throughout a protracted bear market within the crypto trade, reeling from the consequences of FTX and Terra Luna’s collapse. In 2024, with the bull market working in full swing, important tokens reaching all-time highs, and novel meme cash driving billions of {dollars} influx into the market, Lazarus’s issues are extra outstanding than ever.
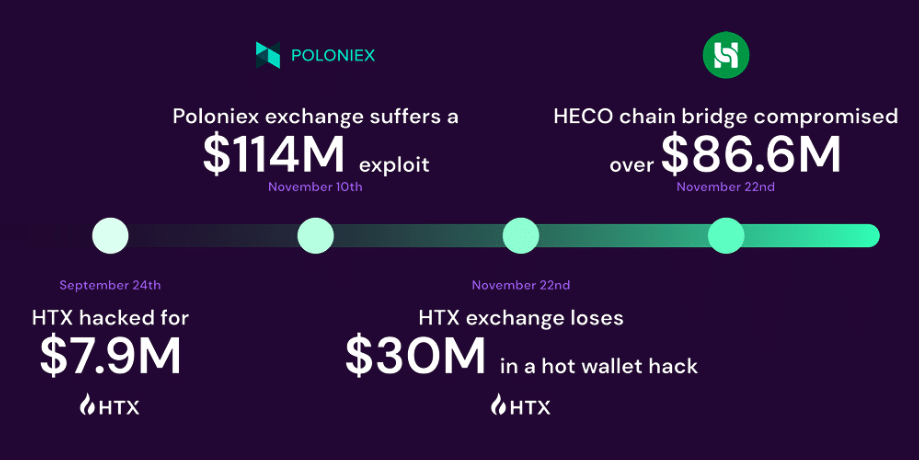
To grasp how the trade ought to put together for such dangers, crypto.information reached out to web3 safety supplier Cyvers, which solely detected the Poloniex hack final yr.
How does Lazarus perform its million-dollar crypto heists?
In response to Cyvers CEO Deddy Lavid, the Lazarus Group has shifted its cyberattack methods considerably in 2023, focusing on centralized entities with a refined and dynamic strategy. Shifting past conventional phishing and brute pressure strategies, the group now employs AI-driven phishing campaigns and complicated sensible contract exploits.
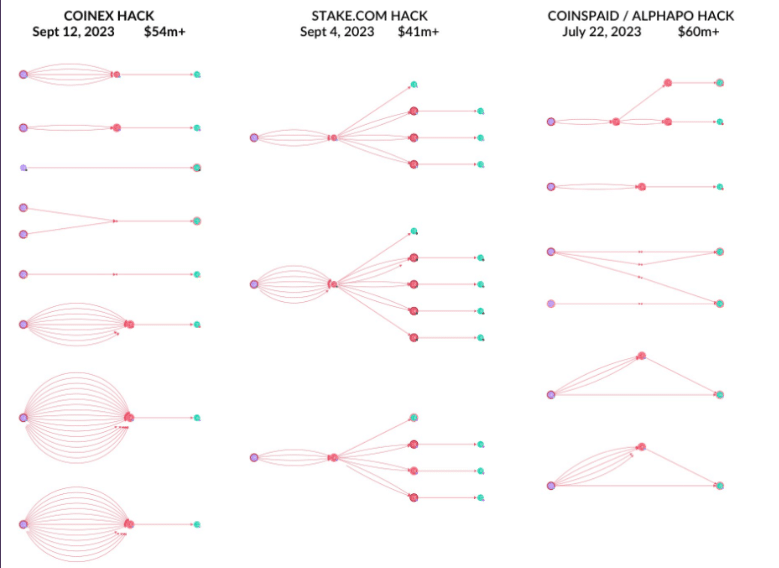
Particularly, the assaults on Poloniex and HTX targeted on stealing non-public keys and launching a sequence of small assaults in a brief interval. The group additionally used pre-programmed bots to run automated assaults. The bots are inclined to dwell in a system for a very long time undetected earlier than beginning to exfiltrate the property.
Lavid additionally talked about that Lazarus Group’s operational strategies resemble army precision, reflecting a uncommon stage of professionalism amongst cybercriminal syndicates. Lavid outlines a recurring sample of their assaults: preliminary infiltration by social engineering, remaining dormant throughout the goal group for months, and stealing non-public keys for a sequence of fast, well-orchestrated assaults involving dry runs and quick, anomalous transaction charges.
The preparatory section is adopted by dispersing the stolen property throughout a number of blockchains, ultimately funneling them by mixers or exchanges for laundering.
So, whereas the crypto bull run of 2024 presents an exhilarating prospect for buyers and innovators alike, it additionally presents an pressing name to arms for the safety sector.
“My evaluation emphasizes the necessity for elevated safety measures within the cryptocurrency and blockchain house, urging a deeper recognition of knowledge safety’s significance, a name for extra safety professionals, and a give attention to proactive assault prevention.”
– Deddy Lavid, CEO at Cyvers
In 2024, Lavid foresees a crypto market that outgrows its nascent vulnerabilities to undertake a extra mature strategy to safety.
Crypto platforms must allocate higher sources in direction of creating safety experience inside firms and a holistic technique that preempts assaults and comprehensively addresses potential fraud throughout the blockchain.

